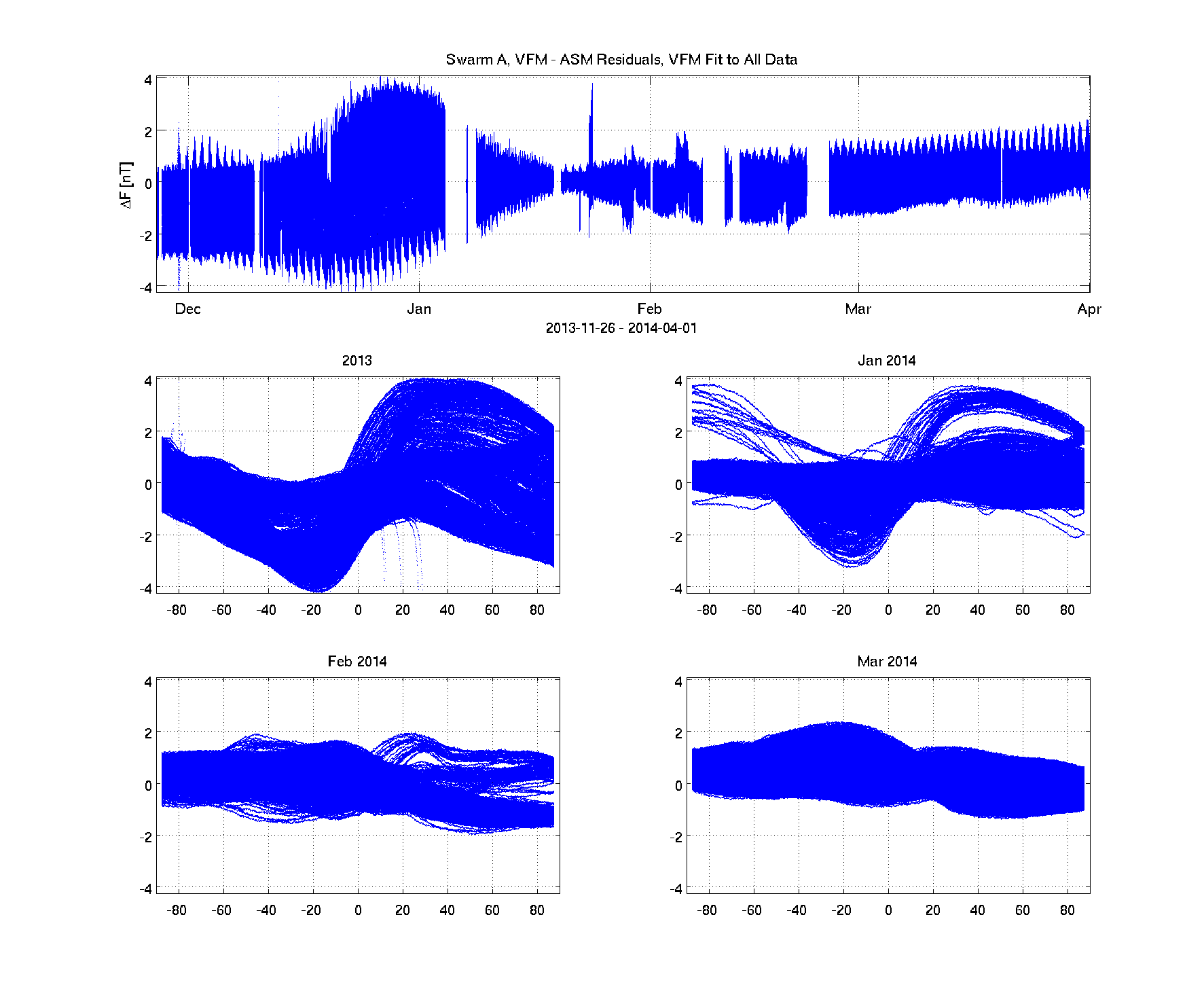
Swarm data covering the period from launch until end of March 2014 have been analysed by fitting parameters for the VFM instrument using all or selected subsets of the data. In general, VFM parameters cover scales, offsets, and in some cases the non-orthogonalities of the three VFM sensor axes, i.e. a "usual" total of 9 parameters.
The overall rms is 1.045 nT; the non-orthogonalities agree with pre-flight values within 8 arc-seconds. I.e. we see a general very good stability but with significant, systematic residuals in particular until mid January.
Limiting the data to periods of eclipse (defined by solar array bus currents being zero) improves the statistics to around 0.55 nT. Further rejecting outliers (residuals above 1 nT) and simultaneously fixing the non-orthogonalities to pre-flight values, yields the following result:
The data are available in SwA_dF.mat (467 MB).
In order to check the possible dependency on the temperature of the VFM electronics unit (EU), a fit including linear dependency of scales and offsets with the electronics unit temperatures have been performed. No big improvement of the residuals is seen:
No delay of the temperature measurement have been applied in this analysis.